Science - Nature - Cosmology - Muses and More
Black Holes
Item from the Energy Syndicate
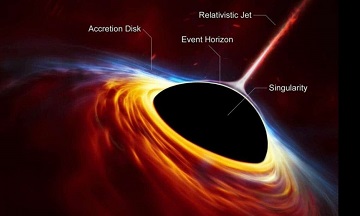
It is only a few decades ago when Black Holes were purely theoretical. In more recent years, observations detected phenomenon that strongly indicated the presence of Black Holes and within the last decade Black Holes have been photographed. The Chandra X-Ray telescope has revealed a Universe with many of these mysterious places in space.
The current science of black holes is expanding and diverging into niche areas. This piece is going to introduce some of the areas of discovery and investigation.
Most black holes are formed by the collapse of large stars. As a star reaches the end of its life it runs out of fuel. This causes an imbalance between the forces pushing out and gravity pulling in. When massive stars reach the end of their lives, they collapse in on themselves. Some explode as Supernovae but some continue to collapse in an unstoppable way that forms the black hole. Some black holes are formed by the merging of black holes, causing the creation of a new one.
There are two main classes. A supermassive black hole and a stellar mass black hole. The measure of a black hole concerns the material, it’s mass, describing it in terms of stellar masses. A stellar or solar mass unit is the mass of the Sun. A supermassive black hole can be between 100,000 to billions of solar masses. These are the type of black holes found at the centre of galaxies. They are huge and can claim a rightful position as galactic architects. The Milky Way’s spin, and character is a result of the supermassive black hole, Sagittarius A Star, at it’s centre. A stellar mass black hole is a lot smaller. The smallest discovered is only 1500 light years from us. It has been estimated to be only 3 solar masses which is extremely small and a bit of a mystery to the scientists; they don’t know how it could have formed - scientists believed that it would require a star of at least 20 solar masses to form a black hole.
The black hole is a place where the gravitational forces are so strong, it is thought nothing can escape it in the traditional sense. Not even light, which is why they are described as ‘black holes’ – they can’t be seen. What can be seen however is the area around the black hole. This area is called the event horizon and is often described as the black holes surface. It is the boundary at which no object or light can escape. Everything is drawn into the black hole at this boundary but the area further out glows hot as material is pulled apart as it is accelerated. This area, the accretion disk, is the area seen in the photographs of black holes.

The first ever picture of a black hole was taken by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT). The EHT was not just a single telescope. It was, and still is, an international collaboration using telescopes around the world to form one incredibly large telescope. To find out more about the EHT, click
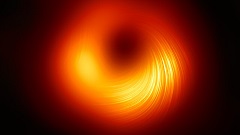
The image to the right, taken in 2019, is of the supermassive black hole in the galaxy known as M87. Sagittarius A Star is the supermassive black hole at the centre of the Milky Way. This was first photographed in 2022. Although the picture was taken quite recently, imaging technology is advancing quickly. The image below is a new image, taken 2024, of the magnetic fields surrounding Sagittarius A Star. M87 also showed strong, defined, magnetic fields which are thought to be responsible for the powerful jet that gets thrown away from the black hole. It really is quite remarkable that it is possible to photograph these objects considering how recently they have gone from being purely theoretical and thought of by many as science fiction.
What happens at the boundary and beyond the event horizon, according to most scientists, is quite strange. It is an area where normal science seems to break down. The maths shows the material that falls into a black hole is drawn into the centre and crushed infinitely. The science, inside a black hole, shows a change of the state of time and distance. Its been said that if a person were falling towards the centre a black hole, they would have as much hope in changing their destination as you or I would in avoiding next Thursday. The spin of a black hole impacts the physics. Mathematicians and physicists appear to have an equal measure of excitement and confusion when ‘doing the math’. The number of theories in this field are being published exponentially. Due to the rapid development of new technologies, it seems likely that there will be no slowing in the field. Kerr spinning black holes are revealing interesting, and sometimes conflicting theories. One indicates that within a black hole there could be entirely new spaces of infinite proportions – are these entirely new eternal places is one question. Another common question in many of the theories and discussions is about what areas can communication take place to and from? Would time travel be possible here? The science also shows that ‘White Holes’ could/do exist. These are thought to be places from which things emerge. There could be small points in space (somewhere in some Universe!) where things would seem to appear from nowhere.
This may surprise some of you, the question of time travel is a subject of serious scientific debate. Albert Einstein's Theory of Relativity introduced to science the notion that time travel, relative to a point in space time would be possible. It is in part based around the principle of large objects bending space-time. Very large objects, such as black holes, bend space-time a lot! Basically, time for an observer just inside a black hole would go a lot slower than for a person far away from any large object, relative to their position. Although this is not possible, if a person could step into a black hole then out again, the universe he would return to would be many, many years in the future – possibly billions! The bigger the object, the bigger the distortion. In February 2024, astronomers discovered an enormous back hole. It was the brightest black hole ever detected. The brightness is a description of the disc, shining brighter than any other yet discovered. The luminosity of this object is staggering – 500 trillion times more luminous than the Sun! It has a mass 17 billion times greater than our Sun, drawing in material at a volume never seen before. It rips apart a mass equivalent to one Sun every day. It is the acceleration of this matter around the hole that emits the light. This area is known as the accretion disc. The data about the hot accretion disc is also staggering. At 7 light years in diameter, it is roughly equivalent to the size of 15000 times the distance of the Sun to Neptune. It is so large, and so bright that it is still visible despite it’s journey of 12 billion light years. An object of this size would cause massive distortion of space-time.

What really happens on the inside of a black hole is not clear. Many theories and the maths lead to different conclusions. Even the premise that nothing can escape black holes has been challenged. Stephen Hawking presented a paper that revealed a theory in which tiny bits of radiation could escape. This is due to an understanding in quantum physics. His conclusion was that all black holes would eventually evaporate away to nothing. The time this would take however would literally be trillions upon trillions of years. Time scales that would appear, to some, to be an eternity – maybe just a blink of an eye to an observer from inside the black hole itself! Stephen Hawking may be right, currently however his theory has not been proven conclusively, and so for now, supermassive black holes will remain the corralling forces to galaxies including our own Milky Way.
Climate Change - What's happening to you?
Item from the Energy Syndicate
If there are any, their numbers will be few; people who have not heard of the concerns regarding climate change. There will be none however who are not being affected by it – whether they realise it or not. For those of you with a keen interest, the principle concerns will be common knowledge. For those of you who aren’t sure, this should help outline some of the basics.
Temperature is the key measure of climate change. The world is an ecosystem. It has successfully maintained a fine balance where life has been able to thrive, in the way life exists in the current time, for hundreds of thousands of years. Over thousands of centuries there are observed changes in climatic conditions which are regarded as natural. Climate change has become an issue of urgent concern over the last 50 years, because the changes that are happening, right now, are dramatic and extreme – the global temperature today is 1.1C warmer than just over 100 years ago. This is having a cascading impact which is set to see a continuing increase in the warming.
The image from the Met Office shows the change since 1850

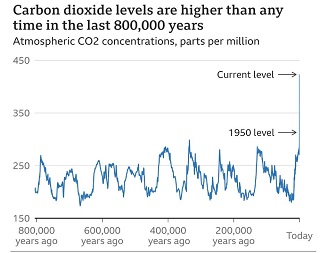
The increase in temperature over the last century does not follow traditional ‘natural’ patterns. It is widely accepted now that the changes are predominately due to human activity, or, entirely human activity. The dramatic changes correlate to the increase in use of fossil fuels; coal, oil and gas. The use of fossil fuels – burning them – releases CO2 into the atmosphere. The levels of CO2 in the atmosphere has increased by 50% since the beginning of industrialization. CO2 occurs naturally but the increased amounts have the chemical signature that confirms the increase has come from the industrial use.
The concern over CO2 is due to it’s ability to retain heat in the atmosphere. This is why it has been called a greenhouse gas. A temperature rise of 1.1C may not seem like a lot. Globally, it is having a dramatic impact; reducing Arctic sea ice, melting glaciers, ocean warming, increasing sea level and increasing the frequency of extreme weather.
In 2023, rising temperatures saw records being repeatedly broken. Some areas have suffered more than others but the trend is firmly upwards. Life in the sea and on the land is being impacted. NOAA – National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration – produce detailed data which is as undeniable as it is sadly prophetic.

NOAA have an observatory on Mauna Loa, Big Island, Hawaii. The data from the observatory acts as an accepted global benchmark for the measurement of CO2 in the atmosphere. The carbon in the atmosphere is 50% higher than pre-industrial levels. It has reached levels not seen for millions of years.
“The science is irrefutable: humans are altering our climate in ways that our economy and infrastructure must adapt to. We can see the impacts of climate change around us every day. The relentless increase of carbon dioxide measured at Mauna Loa is a stark reminder that we need to take urgent, serious steps.” Rick Spinrad, NOAA Administrator
There are sadly many aspects that could be looked at to illustrate the impact of global warming but to simplify things we are going to look at just one; the rising temperature in the arctic which the Energy Syndicate reported on in the summer of 2023.
The Arctic is warming faster than any other region in the world. In the summer, the surface air temperatures were the warmest ever recorded. The sea ice has reduced to the lowest level ever recorded. The changes in climate are affecting the entire ecosystem including the people and communities. The average sea temperatures in August were 5 to 7 degrees Celsius higher than the 20 year average. The year saw record breaking precipitation which contributed to the snow cover in North America setting a record low in May.
NOAA insist that immediate, meaningful action is needed but seem at a loss as to how to make themselves heard effectively.
"We have known about this for half a century, and failed to do anything meaningful about it. What is it going to take for us to wake up?” Pieter Tans – Global Monitoring Laboratory
"It’s depressing that we’ve lacked the collective will power to slow the relentless rise in CO2. Fossil-fuel use may no longer be accelerating, but we are still racing at top speed towards a global catastrophe.” Charles David Keeling – Scripps Institution of Oceanography
The polluting of the ecosystem with CO2 and the resulting climate change are an embarrassment, in the first instance, for the human race. However, the issue is turning into an indefensible disgrace as wisdom increases, but globally there is a failure to react effectively.
Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation
Item from the Energy Syndicate

The Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC) has made headline news recently (July 2023) due to research suggesting that it may be about to collapse in the next 80+ years but this could be as soon as 2025. The research and data is complicated. For those of you with a detailed scientific interest, this link with video lectures may be of interest to you: AMOC Lectures
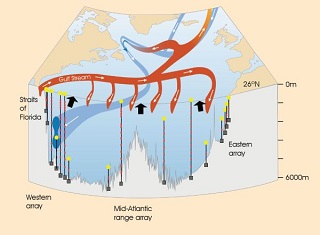
AMOC is a large system of currents which stretches from the Tropics into the North Atlantic. The interactions are complex and not fully understood but in general it acts like a conveyor, carrying water from the tropics northwards. It is driven by differences in water density mainly due to temperature and salt content. Warm water flows northwards, cools, some evaporates which increases the amount of salt and as a consequence of this journey the density increases. The denser water sinks deep into the ocean. The cold dense water begins to move southwards and spreads out several kilometres under the surface. As the flow moves southwards ‘upwelling’ occurs which is a process that sees the colder water being pulled back to the surface where it warms – completing the circulation. This global process continually mixes the worlds oceans, distributing energy around the earth contributing to the climate we experience.
Although this is a basic picture of the AMOC, there is no clear stream; it is a lot more intricate than just a simple single stream. It was in 1985 when the first paper was published voicing concerns about the AMOC and the possibility that it could collapse. However, it was not until 2004 that saw oceanographers continually measuring the AMOC. Other solid data has been gathered from the palaeo record which has both historic and contemporary interpretations – the last time there was a rapid change was around the end of the last ice age.
The data gathered shows that the AMOC has regular changes from year to year but what causes the changes is a matter of debate. The climate models demonstrate variability and it is thought that external influences, such as greenhouse gases, could be directly affecting the AMOC. The Greenhouse Gases, which are warming the atmosphere and oceans, could be causing an increase in rainfall and ice melt. This increase in fresher water makes the ocean lighter and reduces the sinking action of the conveyor, which forces a weaker AMOC.
The climate models however don’t do ice dynamics very well and so the science seems loose but they all agree that the AMOC is slowing down. The climate models suggest a weakening of the AMOC over the 21st Century, although the majority do not believe, at the time of writing this, that there will be a rapid change during the 21st Century. A weaker AMOC, as opposed to a rapid change or collapse, would carry less warm water to the north. This reduction would likely serve to offset the warming affects of greenhouse gasses over western Europe. The modelling however still shows an overall warming.
The new research is suggesting the AMOC could collapse. Although most of the scientific interpretations don’t believe there will be a collapse of AMOC, there is agreement regarding what will likely happen if it does collapse. A shutdown would cause the northern hemisphere to cool and a sea level rise in the Atlantic. More winter storms over Europe and increased rainfall around the Mediterranean would also be expected as well as a potential impact upon the Asian Monsoon and El Nino. This would only happen if the AMOC threshold is crossed. The threshold is basically a point when freshwater has increased to such an extent that the circulation ceases. Although the AMOC could recover in the early stages (less than 20 years of increased freshwater reversed rapidly), if the state persists pasts the threshold, it is thought that the AMOC can not recover, (increased freshwater for circa 50 years), even if the level of freshwater decreases after this period. An AMOC shutdown would have disastrous consequences for the ecosystem.

The Big Bang
Item from the Energy Syndicate
The Big Bang is a term widely used nowadays to describe the origins of the Universe. The Universe itself is thought by scientists to be every aspect of our existence; encapsulating everything, all matter, everything that is known, everything that can possibly be, including time itself. Estimates by scientists indicate the Universe is 13.8 billion years old. Its worth noting that the idea of the Big Bang was first put forward in the 1930’s, which, at the time, represented a radical step away from the orthodox mainstream thinking. The theory is now widely accepted by most scientific fields but that does not preclude the scope for further radical shifts in the future.
Although there is a current view of how many galaxies there are, and how many stars the Universe contains, it seems pointless writing it here as the numbers increase regularly and it is certain that the vastness will continue to reveal more and more. Suffice to say, there are hundreds of billions of galaxies in the known Universe, each containing hundreds of billions of stars – mind boggling!
There are numerous theories about the origins of the Universe but the Big Bang, as a single explosion, as the originating cause of the Universe, is mostly accepted. What happened just after (...and before), is the subject of lively investigation. NASA describe an explosion reaching temperatures of possibly 10 billion degrees, causing space and time, energy and matter to be propelled at an impossible speed, causing an equally, seemingly impossible, expansion of the Universe – a near instantaneous emergence of existence. ‘Why’ the Big Bang, that spark of existence, happened is out of reach of any science – a true mystery, in keeping with many of the old and newer creation stories, myths and scriptures.

What happened just after the Big Bang, and evolution of the Universe since, is a subject of investigation for the cosmologists. What many agree upon is an afterglow appeared around 380,000 years after the Big Bang. This afterglow has been called the Cosmic Microwave Background, CMB – first discovered in the 1960’s. The CMB shows up in the microwave part of the electromagnetic spectrum and so can’t be seen with the naked eye. If it could be seen it would show up as a uniform light in every part of the Universe. This is thought to be the oldest light in the Universe.
Studying the CMB is one of the highest priority investigations in cosmology. Projects to get a clearer image of the CMB use earth and space based telescopes. Currently there is a project underway to greatly increase the sensitivity of the searches by using a combined network of small and large aperture telescopes sited in Chile and the South Pole. The project, called “Cosmic Microwave Background Stage 4”, is expected to increase data sensitivity ten times more than it has been. There are 121 worldwide institutions and over 400 scientists involved in the CMB-S4 collaboration. They believe the CMB will hold the key to understanding what the Universe is made of and the life story of the Universe – including the intriguing goal of looking for evidence of cosmic inflation. Looking through the telescopes is like looking back in time to almost 14 billion years ago. Despite past certainties that the expansion of the Universe would be slowing down due to gravitational forces, research has demonstrated that the expansion of the Universe is speeding up. This expansion has added momentum to the thought that dark matter could be responsible. The science behind this is at the cutting edge but seems to present more questions than answers to the scientists as they struggle to apply the laws of gravity; resolving the inconsistency between general relativity and quantum mechanics. The Universe contains an estimated 5% matter. The aspects described by science as ‘Dark’ are a lot more abundant, and there is possibly more unknown to which gravity has no grip. The CMB-S4 collaboration may indeed achieve its goals but with such an increase in data, they may find themselves heading in new directions, getting excited about things that are not currently expected – As the cosmologists may tell you, “Watch this Space!”
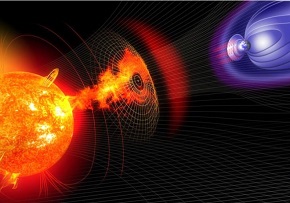
The Solar Cycle - a storm is coming...
Item from the Energy Syndicate
The Solar Cycle is the term used to describe the observed regular pattern that our Sun goes through. The regular patterns see Solar activity increase and decrease from a ‘solar minimum’ to a ‘solar maximum’ phase. The Sun generates a huge magnetic field and, like the Earth, has a north and south pole. During the solar maximum phase the poles flip, seeing what was the south pole becoming the north and the north becoming the south pole. These poles then remain as they are until the next solar maximum phase when they apparently flip again. The solar cycle has been observed to be approximately 11 years but this is an average and can fluctuate. To date, observations have seen a cycle as quick as 8 years and as long as 14 years. The solar cycle is characterized by the intensity and frequency of solar activity. Sunspots, solar flares and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) all increase around the Sun’s solar maximum.
The hot, electrically charged gas of the Sun creates a powerful magnetic field. In the areas where the magnetic field gets particularly strong, dark patches emerge. The dark patches, which are cooler than the surrounding area, are known as sunspots. The sunspots are the visible signs that underneath the conditions are getting stormy, with magnetic fields getting intense and twisted. The more sunspots there are, the more solar activity there is. These increase as the Sun moves to a solar maximum.
Solar flares are linked to the sunspots. They produce bursts of light and x-ray radiation. This happens when the concentrated, twisting, magnetic fields reconnect in explosive fashion. The classification of Solar Flares, going from least to most intense is: B, C, M and X. M-class Solar flares can cause radio blackout and risk to astronauts.
Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs) are clouds of particles that come from the Sun at millions of miles per hour. Quite literally pieces of magnetic energy that have become unstable and erupted from the Sun. Once again, the CME’s have sunspot origins. The intensity of the solar wind streams also increases at the times of increased solar activity.
The solar cycle and increased solar activity affects space travel, technology and weather here on Earth. The level of impact depends upon the intensity of the events in the solar cycle. When the solar maximum is not too intense, sometimes described as ‘wimpy’, there is less impact on the weather and can see a reduction in global warming. The last solar maximum in 2014 was described as 'wimpy', and is thought to have been an aid in keeping the rise in global temperature down. The predictions for the next solar maximum has been predicted to be ‘wimpy’ also.
In 2022, The Voice, predicted 2025 would see satellites falling. Although the scientists are currently expecting a ‘wimpy’ solar maximum in 2025, ‘The Voice’ is claiming 2025 will see an intense period of solar activity. This period is going to be a time of considerable concern. The increased solar activity will see a rise in global temperatures, coinciding with a strong El Nino event which also contributes to warming. The space weather is going to affect satellites. The systems that rely on satellites are going to be tested more than most at this current time (Spring 2023) expect. As much as telecommunications may seem of great importance, the state of life itself will emerge as the focus for the hearts and minds of the world. There is less time to change than many of the money and business orientated would like. New ways have to be found quickly. There is no more time for clever arguments.
The Oort Cloud - What is it?
Item from the Energy Syndicate
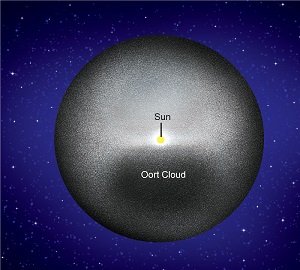
The Oort Cloud is a term used to describe the theoretical cloud that occupies the most distant region around our solar system. Its size is from about 2000AU from the sun at its inner edge, with a thickness that extends to a distance almost half way to our nearest star neighbour, Alpha Centauri. The cloud forms a shell around the solar system as opposed to a flat disk. The shell is made up of ice, consisting of mainly water and methane, and space debris. Although some of the ice is thought to be the size of mountains, the objects in the Oort Cloud are too small and distant to observe clearly, despite the trillions of objects it is likely to contain.
Scientists have concluded that the Oort Cloud would be the likely source of the comets that have a long period of orbit. Although no object has been observed directly in the Oort Cloud, it is accepted by most scientists that the Oort Cloud exists and is the most logical explanation for the comets.When we think of our own star and solar system, the size can be dwarfed when compared with the figures about the galaxy and universe. Our star, the Sun, is one of billions of stars in the Milky Way and our galaxy is just one of countless billions in the observable universe. Our solar system however, by all reasonable standards is massive. Its outer edge extends to the exterior of the Oort Cloud.
So how big is it?
Although there are no exact measurements, it is thought the Oort Cloud could extend up to 100,000 AU from the Sun. An ‘AU’ is an astronomical unit. Instead of using miles or kilometres, it is easier to express distances in space using larger scales and so AU and light years are used as measures. An astronomical unit is “a unit defined as the distance between the Earth and the Sun, with 1 AU being roughly 93 million miles or 150 million kilometers.”
Neptune is our most distant planet. Light travelling from the Sun takes about 4.5 hours to reach Neptune which is about 30 AU from the Sun. To get to the inner edge of the Ort Cloud, light would take an estimated 28 days to get to it from the Sun. This journey of light through the Oort Cloud is still in its early stages; it is thought that light from the Sun could take up to 1.5 years before it emerges on the far side of the Oort Cloud. To add a bit of perspective to this, the Voyager 1 spacecraft took 3 years to pass all the planets. It has now been travelling for about 40 years at a speed of approximately 1 million miles a day. Voyager 1 will reach the interior of the Oort cloud in about 260 years and take possibly another 30,000 years before it gets to the other side! Our cosmic cocoon is massive.

Knights Templar
Item from the Energy Syndicate
Looking at the picture to the right, you may be forgiven in thinking the view of a street in Royston, Hertfordshire, is without note. For those who know however, they will be very much aware of the unique history that lies beneath. Through a small door, in an alleyway on the right, there is a tunnel that leads down to a cave that remained hidden for centuries. When discovered in the 18th Century, it revealed a site of worship with strong evidence that it was a secret place of the Knights Templar.
The ancient crossroad of Ermine Street and Ickneild Way, marks the location of the caves beneath. They were discovered in 1742 by workmen who were doing construction work above. A millstone was discovered. When lifted it revealed a shaft that looked like a well. Curious about what they had found, they sent a small boy down the shaft. The boy descended using toeholds that had been cut into the chalk. At the bottom he found a man-made cave, cut into a beehive shape filled with debris.
In 1790 a tunnel was made to allow visitors to access the cave easily. The walls of the cave are saturated with carvings. Although some appear to be from an earlier pagan origin, most are Christian, baring all the hallmarks of the Knights Templar. The Royston History Society, who work with Royston Town Council, who manage the cave, say -
“There is a large panel which appears to relate to the death and resurrection of Jesus Christ. Its uppermost carving shows the outstretched hand and arm of God releasing a dove. Immediately below the dove was the body of a shrouded figure of which only the head remains. This may represent the body of Jesus within the Holy Sepulchre prior to his resurrection. There are two crucifixion scenes; a figure believed to be King Richard I (The Lionheart); and a carving with upraised arms, thought to be King David of the Psalms. The panel to the left of King David is most commonly believed to be a memorial to the last Grand Master of the Knights Templar, Jacques de Molay. Elsewhere in the cave are non-Christian carvings, including the figures of a horse and an Earth Goddess, known as a Sheila-na-gig, believed to be Pagan symbols for fertility. Many smaller figures and symbols remain unidentified. A figure holding a skull in its right hand and a candle in its left is thought to show a candidate for initiation and may be a clue as to what the cave was used for. A recent study on the designs of the crowns, swords and costume depicted in the cave suggest that the carvings were likely made in the mid-1300s.” Royston History Society
Although no one can be certain of the caves age and purpose, the most agreed upon theory is that the Knights Templar used the cave for ceremony and prayer in secret. The Knights Templar had a strong presence at the abbey in Baldock. They were a powerful medieval order of warrior monks but towards the end of their power, they were subjected to persecution across Europe. This persecution was largely due to their proscription by Pope Clement V, following the arrest of all the Templars in France by Phillip IV on Friday 13th October 1307. Phillip IV’s keenness to destroy the Knights Templar was most likely driven by his thirst to get hold of the great wealth the Templars had acquired, but his action nonetheless sent a tidal wave through the religious order, driving them underground and away from a position of influence.
When first discovered, there was no great treasure in the cave. There was however a decaying skeleton and a small drinking vessel. Who this person was and the circumstances that led him to be there are a mystery, as is the site itself, but the experience of being there leaves a visitor in no doubt, that the place was held in the minds of those who used it, to be a special and holy space.
The Trees of Life
Item from the Energy Syndicate

There are growing numbers of groups, concerned about climate change, urgently encouraging people to save the trees and plant more. ‘Friends of the Earth’ are looking at a doubling of trees as a minimum measure to bring back balance and avoid a catastrophe. The Woodland Trust say that the UK currently has 13% woodland cover. They estimate this low figure needs to rise to 19% for the UK to meet it’s 2050 carbon net zero target. A target that in itself is likely to prove to be too little too late. They say “There is an urgent need to act now. The UK needs to at least quadruple the current rate of woodland creation and increase the number of native trees. An increase in native trees will help to minimise the pace and level of climate change and adapt to its unavoidable impacts.”
Trees lock-up carbon, reduce pollution and help to prevent flooding. They are also living organisms that are part of the balance of life in the ecosystem, acting as homes and sole providers for countless other living things and instrumental in the maintenance of habitats. The most diverse of these habitats are those that have matured. Planting trees has great benefits but this in itself is not enough; they must be diverse and allowed to age for the full spectrum of a stable eco-community, in all its aspects, to become established and flourish. Protecting ancient woodland, and sensitively expanding it, is to work with what nature has already achieved.

With COP 27 and it’s declarations, there is a hope in many, yet sadly unbalanced with despair, that more talk will amount to good intentions without the force of meaningful action. Individually however, you can show your love for the Earth and the life we know by doing what you can, in whatever great or small ways you are able to, no matter where you find yourself in the world.
If you have a space, try planting a tree and mark it with a plaque – maybe at the same time of a newborn child so they can see it grow as they grow up. For some good advice about planting trees, try clicking this link to the RHS.
If you don’t have space to plant trees, even just telling someone in a chance encounter about the beauty of the world can, in a small way, help to spread the message that the life of the world is special and should be cherished.
Enceladus – The Search for Life – New Research Finds Phosphorus
Item from the Energy Syndicate
The search for life and habitable places in our solar system and beyond is an ever present driving force of scientists in space exploration. One key ingredient looked for is water. Places that have water are potentially places where life as we know it could be, and so the icy moons of the solar system are of particular interest.
Jupiter's icy moons are to be explored soon by ‘JUICE’ – Jupiter Icy Moon Explorer. This is an ESA mission due to launch in 2023. Another moon that is capturing the imagination of scientists is a Saturnian moon called Enceladus.
Enceladus was discovered by William Herschel in 1789. It was named by his son, John Herschel, after the giant Enceladus from Greek mythology. It has a diameter of 313 miles with a mass 680 times less than the Earths Moon.
Enceladus is one of only a handful of places thought to have liquid water beneath a frozen surface in oceans. Enceladus really caught the attention of scientists in 2008 when the Cassini mission captured images of the moon, and observed it spraying jets from its ocean out into space. It has been possible to take samples from this spray. The samples confirmed that many of the chemicals needed for life are present. It is thought that there is hot, mineral rich water flowing from hydrothermal vents which makes it one of the most compelling places for exploration.
The jets from Enceladus have created a ring around Saturn. The moons icy surface is the whitest, most reflective surface in the solar system. The highly reflective surface causes the surface temperature to be extremely cold. Despite a surface temperature of minus 201 degrees Celsius, Enceladus is far from being just a cold inactive rock in space.
Enceladus orbits Saturn between the orbits of two other moons called Mimas and Tethys, and orbits twice for every orbit of Dione, another moon. The proximity of the moons and their regular alignment with the planet cause what is called an orbit resonance. Orbit resonance is when the bodies interact gravitationally. This interaction exerts forces across the moon, causing tidal heating within the moon. Observations of the moon have noted recent geological activity. The poles are almost entirely clear of impact craters, covered with large icy boulders, and have tectonic patterns unique to this region.

The Cassini mission discovered that the jets from the surface are travelling at about 800 miles per hour. The continuous eruptions create a halo of fine ice around the moon and add material to Saturn's E-Ring, albeit a small amount. Most of the erupting material is drawn down onto the moon like snow, ensuring its bright white appearance.
The jets are from relatively warm fractures which scientists have concluded come from an underground ocean. These conclusions are based on gravitational measurements that detect a slight wobble in the moons orbit. The jets themselves exhibit an interesting mix of gasses with organic material that has a density twenty times more than expected.
The jets from Enceladus contain methane, carbon dioxide, water vapour, salts and silica as well as nitrogen gas. The strong evidence for the presence of hydrothermal vents producing heat within the unique chemistry of the global ocean, leads many scientists to believe that Enceladus has all the qualities for a promising potential for life. Currently NASA has a proposed astrobiology mission, called Enceladus Life Finder (ELF) which is intending to assess the internal ocean of Enceladus for habitability.
New research, focusing on the search for the potential for life on Enceladus, has found new pieces of the evolving jigsaw that indicate the oceans inside the moon may be rich in phosphorus. Phosphorus is an important indicator for potential life. It is essential for life’s biochemistry and the key structural component for DNA. It is found in cell membranes, bones and instrumental in the movement of metabolic energy.

This new research is in conflict with previous findings that thought phosphorus would be rare in the oceans. Cassini had gathered detailed data from the geysers but despite detecting organic molecules, phosphorus was notable by its absence. This summer, new research from the University of Science and Technology of China, challenges the earlier findings, claiming that the 2018 research used outdated information regarding the geochemical make-up of the rocky ocean floor. Christopher Glein, of the Southwest Research Institute in San Antonio and co-author of the report, says they have found evidence for the availability of phosphorus in the crust below the ocean. Hao and Gleins research has found the rate that phosphates will be dissolving into the ocean will be higher than first thought. Specifically, the dissolution rate of orthophosphate would be capable of enriching the entire ocean with enough phosphate to support life, in just tens of thousands of years. This rapid accumulation is due to the presence of bicarbonates in the ocean. The researchers believe that increasing phosphorus levels are inevitable, and are confident that they can therefore describe the oceans of Enceladus as habitable.
Currently the researchers hypothesis is lacking direct evidence. With current technology, it will require a future mission to Enceladus to gather data, detecting orthophosphate or phosphorus to provide the meat to the bones of the theory of a habitable, or even inhabited ocean.
Virgin of Hope
Item from the Energy Syndicate

In Seville, located in a working class district, is the Basilica of Macarena. The church is home to a statue of the Virgin Mary. The stature is not just one of the countless statues of the Virgin, it is regarded as one of the treasures of the Church. It has been blessed by the Roman Catholic Church who have given it the title of ‘The Virgin of Hope of Macarena’, which is popularly shortened to the ‘Virgin of Macarena’ or just ‘La Macarena’.
In Seville, La Macarena is regarded as the most revered religious treasure. It is thought that the image was created in the workshops of Pedro Roldan in the 17th-century; there is no exact date, but it is known to have been in existence in 1654. Over the centuries there has been restoration work carried out and items added, resulting in the current form of the statue.
La Macarena (see images), has an extensive wardrobe. The gold embroidery is made from French wire bullion and gold plated tin. The crowns and accessories have been made and remade over the years. The Virgin is seen holding a handkerchief, diamond and emerald brooches, and a rosary. The main body of the statue is made from carved wood. Her tears are made from glass. For most of the year the Virgin of Macarena sits as a centrepiece behind the main alter, adorned with a golden crown and lavish vestments. La Macarena is highly revered, treated as if she is a human being. Any change in garments is done by nuns; the only people who are permitted to dress her.
Once a year, during the most Holy Festival of Easter, La Macarena leaves her place behind the alter and is carried through the streets as the focal piece of the Easter parade.
The holy cross is presented to the crowd and hooded penitents march out of the church.
 For many, the occasion is highly emotional, with an almost electrifying atmosphere as the Virgin reaches the threshold of the church. La Macarena is held at the doorway for a few moments in the night air, with a crowd of faithful onlookers preparing to be witness to a moment of transformation. As the Virgin leaves the church, carried on a throne, it is said that the statue seems to come alive as she moves. The reaction of the faithful is remarkable. It is as though the likeness of the Virgin has become her presence.
For many, the occasion is highly emotional, with an almost electrifying atmosphere as the Virgin reaches the threshold of the church. La Macarena is held at the doorway for a few moments in the night air, with a crowd of faithful onlookers preparing to be witness to a moment of transformation. As the Virgin leaves the church, carried on a throne, it is said that the statue seems to come alive as she moves. The reaction of the faithful is remarkable. It is as though the likeness of the Virgin has become her presence.
As with many things in religion, the celebration is subjected to criticism. Are the crowd worshipping the image, an idol, or are they seeing the statue as a representation of something higher. The faithful however, by and large, do not share these concerns and are in no doubt that something special, something holy is happening.
What is an Ancient Civilization?
Item by the Energy Syndicate
The term, ancient civilization, is used to describe a civilization that has evolved many years ago, often only understood through archaeological evidence. The Sumerian civilization is the oldest civilization known to man, dating from 3300 BC. It is mind boggling to know that there are trees that can live for 5000 years and almost span this entire period, but in the terms of human history, the Sumerian civilization of Mesopotamia is currently recognised to be the oldest.
Between 6000 BC and 1500 BC, significant advances in the development of human civilization took place in Mesopotamia. Small agricultural settlements developed into the world's first cities. Objects found at these sites, including writing and art, have helped archaeologists to create a picture of the lives of the Sumerians and Babylonians; following their journey from villages to empires.
Just Bee Kind

Item from the Energy Syndicate
Many species of bees are in decline. The reasons are largely a result of man's impacts upon the environment. Bees are incredibly important to the pollinating of plants all over the world. If we were to lose the bees we would lose the majority of the plants and flowers that maintain the ecosystem, with a devastating impact upon the food chain.
Set the Controls to the Heart of the Galaxy

NASA picture - released May 2021
NASA has taken a photograph. Not particularly newsworthy in itself, but this picture has been taken over two decades and shows the heart of our own Galaxy
NASA has taken 400 observations with the orbiting Chandra X-ray observatory and combined them with images taken by a telescope in South Africa called MeerKAT. Their new image shows billions of stars, black holes and cosmic structures at the centre of the galaxy in breathtaking detail. Superheated gas and magnetic fields can be seen stretching out from the centre of the galaxy.
Using the two different types of data has produced a fuller picture than ever seen before. The different energies from the X-ray observations are shown in orange, green, blue and purple. The lilac and grey is from the MeerKAT radio data.
The immense magnetic forces form strips which are interacting with each other, forming twists and connections; a similar phenomenon to what is observed around the Sun which is the cause of the space weather that sometimes impacts upon the Earth. The process observed has been called magnetic reconnection. This process plays a major role in heating the gases between stars. These forces are thought to accelerate particles to form cosmic rays. The turbulence caused is thought to be a trigger in the interstellar material to form the birth of new stars.
Mother Earth Day

Mother Earth Day is also known as Earth Day. It was in 2009 when the UN General Assembly, via a resolution, designated April 22nd as International Mother Earth Day. The rationale for the designation of a special day is rooted in a growing global awareness of a need to care for the environment.
It took environmentalists decades to get world leaders to turn and look at environmental issues seriously. The first floundering steps in the 1970’s largely fell on deaf ears. The UN ‘Human Environment Conference’ in Stockholm, 1972, began the political global awareness of the interdependence of life and marked this with ‘World Environment Day’ which is observed on the 5th June.
A Branch of Life
Special thanks to the Woodland Trust for their source material
In the Northern Hemisphere, Spring, if it’s not yet sprung, it is certainly springing! The signs of spring are a delight. Subtle at first and then, almost without warning, an avalanche of renewal, rebirth and transformation.

The emergence of the new leaves on the trees can happen in almost the blink of an eye; one of the true wonders of the season as the canopy reforms. The importance of trees to the balance of life is hard to overstate. To help celebrate the importance of trees we are going to spend some time here with a focus on the Oak tree. Notably the British Oak and their place in history and the environment.
Across the Northern Hemisphere there are approximately 600 species of oak, both deciduous and evergreen. North America has the largest number of species with the United States alone playing host to 90. Britain has just two native species; the common oak (pedunculate) and the sessile (durmast).
In literature, legend and lore, the oak tree symbolises power and strength. Some are up to 1000 years old and so have stood witness to generations of culture, standing silent amongst communities. Oak is celebrated prolifically in writing and poetry up to the present day, and was a firm favourite of Shakespeare. Oak apples, found on oak trees, were used to make ink, and quite literally allowed Shakespeare to put pen to paper. As a building material, oak was very much favoured. It’s strength and its natural bends were perfect for a ships bow or the ‘A’ frame of a pitched roof. St Paul's Cathedral was rebuilt after the Great Fire of London using huge lengths of oak from Sherwood Forest, which still hold firm today. The popularity of oak caused the inevitable decline in numbers. This concerned Queen Elizabeth 1st who ordered a replanting. Her action went some way to alleviating the risk of the total destruction of the oak in Britain.

England is one of the least wooded countries in northern Europe but it does have more ancient native oak trees than the rest of Europe combined. Many of the sites in England contain large numbers of oaks impressively exceeding six metres in girth. Some of the trees are hard to date due to natural hollowing - shedding the dead inner heartwood in a symbiotic relationship with fungi and invertebrates. The hollowing creates a compost which is good for the tree but does not help with counting seasonal rings. Quite often there is very little difference between an oak that is, for example, 600 years old and 700 years old. One of the highlights of the Sherwood Forest experience is the ‘Major Oak’, made famous by Walt Disney in Robin Hood. Looking at a picture of the ‘Major Oak’ taken in 1915 and comparing it to
 another taken in 2016, the only noticeable difference is one picture is in colour and the other is in black and white – it seems almost timeless. Art work and written accounts are sometimes used to assist with dating when scientific techniques struggle due to the lack of material caused by hollowing. One question is, ‘why do so many sites exist in England of ancient oak with a six meter girth and above where almost none exist in northern Europe?’
another taken in 2016, the only noticeable difference is one picture is in colour and the other is in black and white – it seems almost timeless. Art work and written accounts are sometimes used to assist with dating when scientific techniques struggle due to the lack of material caused by hollowing. One question is, ‘why do so many sites exist in England of ancient oak with a six meter girth and above where almost none exist in northern Europe?’
The Sun
The Sun is a 4.5 billion year old ‘yellow dwarf star’. It is without doubt the most important celestial body significant to life on Earth and everything we do as humans. It is impossible to overstate how important it is. To look at all aspects of what the sun is instrumental in would take a lot more space than permitted here for this article and would fill library after library if such attempt was made.
Our focus here is to look at some of the key facts about the anatomy of the sun as understood by science at this present time.
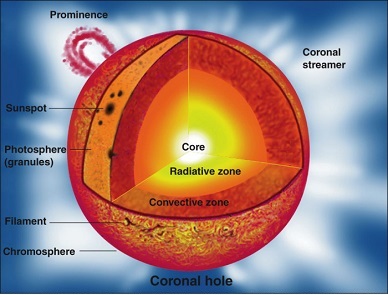
The Sun is massive. Although there a lot of other types of stars which are a lot bigger, the Sun comprises 99.8% of the Solar systems mass. All stars have to be big. Without the minimum critical mass necessary they would not be able to form as stars. If you take our Sun as the measurement for 1 unit (1 solar mass), it is thought that the minimum mass at which a star can form is 0.08 solar masses. To put this into context, Jupiter is about 0.001 solar masses. Even the smallest stars have to be massive to become stars.
Due to its size and mass, the Sun’s gravity exerts forces across the entire solar system holding everything in place such as the Earth and its orbit. When stars form, gasses collapse in on themselves which cause the star to ignite and draw in more of the material around it, adding to its mass. The debris that remains is significant in the formation of the planets. Gravitational eddies cause material to collect which over time gains mass and draws greater quantities of material in. Planet formation is very much subject to the forces of the host star – in our case, the Sun.
The Sun itself is not just a uniform ball of burning gas. It does have an anatomy. Because it is gas, areas within the Sun rotate at different speeds. The mass of the Sun is held together by gravitational forces. Its size creates immense pressures and temperatures especially at its core where its temperature is about 15 million degrees Celsius.
The Sun has six distinct regions. Three of the regions are on the inside of the Sun: The core, radiative zone and the convective zone. The other three regions are: The photosphere, the chromosphere and the corona which are all visible on the surface.
The core is the part of the Sun which is hot enough to sustain thermonuclear fusion – where hydrogen atoms fuse to make helium. A process that releases massive amounts of energy. This process in the core powers the Sun and is responsible for all the heat and light emitted. This energy is released to the radiative zone through radiation. It finds its way towards the convective zone but is thought to take 170,000 years to get there! The convective zone is the area of bubbling hot plasma moving to the surface of the Sun. In the convective zone the temperature is lower – less than 2 million degrees Celsius but still hot enough to boil diamonds.
The outer layer of our gassy Sun is called the photosphere. This is the layer from which most of the Suns radiation escapes outwards as what we see as sunlight. It’s temperature here is about 5,500 degrees Celsius. This radiation passes through the Suns atmosphere which is made up of the chromosphere and the corona from which sunspots and solar flares can be seen emerging. Outward from this area it has been observed that the temperature increases to around 2 million degrees Celsius. The reasons for this is a matter of debate - one thought is that it is due to the displacement of kinetic light from the core. The truth behind this and more should soon be supported with extensive data coming from ESA’s Solar Orbiter mission launched last year. It has already taken images at a point nearer to the sun than anything before and is set to deliver insights into the Sun like no mission before.
This is SETI calling...
60 years of searching – item by the Energy Syndicate
For one week in April 1960, Frank Drake thought he had discovered aliens.

At the National Radio Astronomy Observatory in Green Bank, Drake pointed a new 26 metre telescope at the star Epsilon Eridani. The telescopes readout went crazy – the speaker connected gave off a string of strong pulses which Drake thought was clear evidence of an alien intelligence.
Rather than being from another world, the signal was home grown. Since that week, Frank Drake has detected no signal that is thought to be from another world intelligence.
An assumption that a more advanced, or as advanced, civilization is going to be one that has surrounded itself with technology as the human race has, is to assume something that is so narrow in scope that a search for such life in that way really limits the imagination and practicalities of such a search.
A message targeted at the Orion Nebula, for example, would take 1350 years to get there at light speed. If there was a mechanism by which a civilization could receive the SETI blast what would they think of it?
An advanced civilization may have developed different ways of communicating. They may respond if they get the message and feel inclined to do so – maybe for reasons of curiosity, need or care. A response however may be in ways that are more personal and immediate than any “around the houses” type methods that SETI is employing.
While science remains trapped in the physical, holding onto barriers of speed and distance, the success of the methods used, hoping for contact, not only remain unlikely but also preclude the chance that SETI will even notice clear messages and contact that take a different form – something outside their technological assumptions.
Will SETI ever receive a reply? Maybe… Maybe not. Will someone on Earth be there to hear the reply above the noise that is being increasingly produced? Using the same technology, if a message was received in the Orion Nebula, which is an example in our cosmic neighbourhood, it would take 2700 years to receive a reply if an intelligence was to immediately reply using similar technology. The chances are SETI will not receive a reply from the Orion Nebula because SETI will most likely no longer exist. Even if an intelligence does reply, what would they say? “Hi” and wait for another 2700years for a response?
Modern humans don’t have a great track record when going on voyages of discovery – the initial delight often results in an assumption of conquest, pollution and then destruction of the environment. The human race at present are like the noisy neighbours with a burning car in the front garden – would you like to invite them around? Maybe a message will get to another world but it will be the life matured that gets a response – in the meantime maybe the most Frank Drake can hope for from a life matured is “Sorry we were out when you called – no designated safe place was specified”.
Hydrogen Atom
Unique among the elements – item by the Energy Syndicate
Novembers Ramblings talked quite a bit about atoms and the elements. This piece expands on that to give some wider understanding.
The birth of the universe as described by scientists sees hydrogen  as one of the first elements to form and then helium. It is thought that the conditions that existed before this time were too hot and too dense for elements to have formed.
This science however does not explain anything about the originating conditions prior to ’The Big Bang’ other than there is no scientific language to describe it.
as one of the first elements to form and then helium. It is thought that the conditions that existed before this time were too hot and too dense for elements to have formed.
This science however does not explain anything about the originating conditions prior to ’The Big Bang’ other than there is no scientific language to describe it.
An element is a substance than cannot be broken down into a simpler substance by ordinary processes. There are 92 naturally occurring elements as far as science can determine based upon the evidence in the observable universe. Hydrogen is the lightest of all the elements. It is the first element on the Periodic Table. Hydrogen's element symbol is an ‘H’, its atomic number is 1 and it has an atomic mass of 1.008. It was Henry Cavendish in 1766 who discovered hydrogen although Antoine Lavoisier who got most of the credit and is responsible for the name the element has today.
Elements which have the same atomic number but a different mass number are called isotopes. Hydrogen is present in three natural forms - Protium (1H), Deuterium (1H2) and Tritium (1H3). Protium is the most abundant form of hydrogen, making up 99.98% of all the naturally occurring hydrogen.
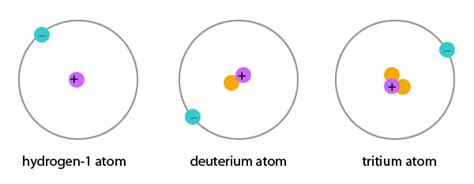
Hydrogen (1H) has 1 proton and 1 electron. Add 1 neutron and Deuterium is produced. Add 2 neutrons and tritium is produced. The processes that make it possible to ‘add a neutron’ only occur naturally in the hearts of stars. Hydrogen makes up 75% of the element mass of the universe. Its abundance and properties are of great interest to those looking at developing new clean sources of energy – burning hydrogen produces water.
Hydrogen atoms, like other atoms, are made up mainly of empty space – 99.999999% empty space and ‘quantum fog/fuzziness’. Atoms are the smallest natural units that make up the elements. It would take approximately 100 million hydrogen atoms placed in a line to make 1cm. Every atom has a nucleus and a number of electrons depending upon the element/substance. At the atomic level, classical physics struggles to predict behaviour – the quantum effects at this level saw the rise and development of quantum science. The nucleus of atoms are made up of protons and neutrons except the most abundant form of hydrogen which has only 1 proton – this is one unique quality of hydrogen.
Life on Venus?

Signs of life on Venus - Report from the Energy Syndicate
Anyone who is even remotely interested in astronomy and the solar system could not have missed the news that scientists have discovered signs of life on Venus! The news has come as a total surprise to scientists who previously believed life on Venus would be impossible.
Venus is our planetary neighbour. It is the 3rd brightest object in the night sky. The surface temperature on Venus is 872 degrees Fahrenheit which is hot enough to melt lead. It’s thick atmosphere has clouds of sulphuric acid, hurricane force winds and a pressure 90 times that of Earth - roughly the same pressure we would find 3000 feet underwater. The environment is extremely inhospitable and yet it would appear the detection of phosphine in the upper atmosphere of Venus is a positive marker of life.
On the 14th September 2020, a team of astronomers from Cardiff University announced the news to the world that they had discovered signs of life on Venus. The team was led by Jane Greaves. For over a year they had been looking for phosphine initially using the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT) - a sub-millimetre-wavelength radio telescope at the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii. Using the JCMT the team looked for the absorption features coming from Venus. Phosphine has a very specific absorption frequency. The team found that there was indeed Phosphine in the upper atmosphere. Phosphine is a bio-signature for life. The chance that the amounts of Phosphine have been created by a chemical process has been largely discounted because anything other than a life process does not produce the quantities that have been observed. Phosphine breaks down in just a few hours and so scientists are certain that what they have observed is being created continually – most likely by anaerobic bacteria which put out Phosphine as one of their waste products.

The main bulk of the life signatures are located in the mid-latitudes, reducing towards the poles. Its thought that the bacteria exist high up in the atmosphere where the temperatures are between 20 and 30 degrees centigrade. The nature of the life is a matter of debate. Due to the high concentrations of sulphuric acid, scientists are struggling to imagine how the life manages to survive but it could be because the life has a significantly different bio-chemistry than that found on Earth.
What is particularly exciting to the researchers is that if life on Venus is confirmed, it means it is highly likely that life does exists and is evolving elsewhere in the galaxy and Universe. The argument is that a completely separate bio-genesis on our neighbouring planet makes it almost statistically impossible for there not to be life elsewhere. That viewpoint however looks at the constituent parts – it could be that life is more interconnected than science accepts at the moment and the growth of life within the galaxy for example is as much a bio-genesis as what is seen for an individual planet at present.
Titan
Is it a future home? Item from the Energy Syndicate
Titan is the largest of Saturn’s moons. It is the second largest moon in our solar system. The largest moon, which is 2% larger than Titan, is Jupiter’s moon, Ganymede.

Titan orbits Saturn at a distance of about 759,000 miles which is itself about 886 million miles from the Sun. With a radius of about 1600 miles Titan is larger than Mercury and about 50% larger than our own moon. Due to its distance from the Sun, the sunlight is about 100 times fainter than that on Earth and it takes about 80 minutes to reach it.
Titan is the only moon in our Solar System to have a thick atmosphere. The thick atmosphere is mostly nitrogen like Earths and contains methane as well as small amounts of carbon rich compounds. This atmosphere gives a pressure 60% greater than that of Earth and extends to an altitude ten times higher than Earths. Titan's atmosphere makes it appear a golden orange and is difficult to see through. By using different wavelengths, (see image) the NASA/ESA Cassini-Huygens mission was able to look through the atmosphere to gather data and images as well as Huygens’s amazing images and science from the moons surface during and after descending safely.
Titan is the only known place, other than Earth, to have liquids in the form of rivers, lakes and seas with a liquid cycle similar to the hydrological cycle on Earth but with liquid hydrocarbons like methane and ethane. The mission discovered what is thought to be an ocean of water, not methane, beneath Titans thick icy crust.
Titan's orbit around Saturn is tidally locked in synchronous rotation which means the same side of Titan is always facing Saturn. Saturn’s orbit of the Sun takes 29 years. Saturn’s axis is tilted, like Earths, which in turn sees Titan tilted in relation to the Sun and so there are seasons on Titan. Each season lasts about 7 years. The seasonal changes add to the dynamic qualities of the moons liquid and weather cycles. Despite being -179 C at the surface, the liquid cycle sees clouds, rain, evaporation and erosion. Titan is one of the most Earth like places in the Solar system.
The NASA/ESA Cassini-Huygens mission discovered that Titan has all the building blocks thought to be essential for life. It's quite possible that life as we know it could exist, now or in the future, in the subterranean water seas. It is also possible that the surface oceans could hold life but certainly not as we know it. At this present time, Titan could not be described as a home from home but this may change over time. One thought is that as our Sun gets older and enters a red giant phase, the expanding Sun will deliver more light and heat to the surface of Titan. This would cause a significant change in the atmosphere and potentially a more suitable environment for life as we know it.
Betelgeuse
Red Supergiant. Item from the Energy Syndicate
Betelgeuse is a star known as a red supergiant. At 724 light years away it is the nearest red supergiant to Earth and the one that scientists believe will go supernova soonest. Betelgeuse can be found in the night sky by looking for the Orion constellation. Move your attention from Orion's belt (the 3 stars in a line) to the upper left – it is the star that is red.

It is possible that Betelgeuse has already exploded – due to the distance, if it exploded in 1726, we wouldn’t observe it here on Earth for another 430 years in the year 2450. Betelgeuse is massive. If it was placed in the centre of our solar system it would extend almost to Jupiter. A red giant forms towards the end of a stars life. Due to Betelgeuse’s size it is massive enough to go supernova. A supernova is a powerful explosion at the end of a stars evolutionary stages. The energy released gives off a greater luminosity than the entire galaxy. The star either becomes a neutron star, black hole or is completely destroyed. This end of the star sees it producing a huge amount of material with heavy elements, such as gold, being forged in the last moments.
One reason scientists believe Betelgeuse is likely to be the next red supergiant in our local vicinity to go supernova is because of its fluctuating luminosity. Betelgeuse was always seen (by humans) as one of the brightest stars in the night sky and easy to see. In recent years Betelgeuse has been dimming. It dimmed to such an extent that it was downgraded as one of the brightest stars. It dropped by 40% of its normal value during autumn and winter 2019/2020. Since then it has recovered but the fluctuations point to an impending supernova explosion. The explosion will cause the brightest light in the sky other than the Sun. We are not in any danger from this explosion but the waves in light and gravity will certainly be felt on Earth.
Tardigrades
Amazing little creatures. Item from the Energy Syndicate

Tardigrades, sometimes called Water Bears or Moss Piglets, can be as much as 1mm in size but most are less than half a millimetre. They resemble miniature vacuum bags which have sprouted 8 limbs with claws. Often described as ‘cute’, these creatures have brains, eyes and nervous systems. There are 850 recognised named species but there are thought to be many more that have yet to be given a name.
Tardigrades like wet or aquatic areas but can be found all over the planet. If you want to find some to observe just get some moss, soak it for 20 mins then ring it out into a dish. When the mud settles you should see a number of creatures. A magnifying glass will help if you don’t have a microscope – the tardigrades are the ones that look like squat caterpillar type creatures.
They are of particular interest because they posses some unique abilities. From a scientific point of view they are probably the toughest animal on the planet. Most animals can not survive for very long without water. Tardigrades however can dry up completely and exhibit no bio-chemistry at all but when water is added they come back to life with no harm at all.
When totally dried up they roll into a ball called a ‘Tun’. Cryptobiosis is the ability to replace water with proteins and suspend metabolism. The Tardigrades can remain in this state for decades but when in water again they just spring back to life unharmed.
Tardigrades are described as extremophiles. This is because of their ability to survive some of the most hostile environments imaginable. They can survive: 6000 atmospheres of pressure; -272.95 Kelvin which is almost absolute zero; heat of 148 centigrade; excessive concentrations of most gasses; 20 times the level of radiation that we can survive and have even survived the vacuum of space, brought back to earth and revived! The little water bear puts its existence on hold in its Tun state and shows no signs of life – Its alive, then not alive then alive again. Imagine the confusion if Schroedinger had used the Tardigrade instead of a cat?
One question that has arisen in the study of Tardigrades is what happens to memory during this process – is it intact when rehydrated? The special abilities of the Tardigrades is being researched. There are trials going on at the moment to use the Tardigrade tech to extend the life of blood platelets and vaccines in transport and storage that will extend the shelf life from a few hours or days to maybe years.
The Tardigrade tech is also being looked at in the field of space travel. Researchers are looking to see if some of the Tardigrade tricks can be adapted to assist astronauts in physically surviving long journeys such as missions to Mars.
Creative Explosions
Item selected by the Energy Syndicate

A Neutron star is created when giant stars go supernova – their cores collapse, melt the protons and electrons into each other, forming neutrons. They are approximately 20 km in diameter and become so dense that just a teaspoon full of their matter would weigh a billion tons. The average gravity on a neutron star is estimated to be about 2 billion times stronger than that on Earth. They are very alien, spinning up to 43,000 times per minute with some ejecting jets of material at nearly the speed of light. When the jets are spinning and pointing at the earth the pulses can be easily detected – scientists call these pulsars. The pulses are so regular and predictable that some are used in the same way that a scientist would use an atomic clock.
Neutron Stars can orbit each other but if they get too close they get drawn in together and collide. In 2017, gravitational waves caused by two neutron stars colliding were detected on Earth. The research also provided evidence that neutron star collisions produce much of the Universes heavy elements such as gold and platinum although scientists continue to debate which of the cosmic events provide the bulk of heavy materials in the Universe.
When neutron stars merge they produce a massive amount of materials which are thought to be the substance of later forming solar systems. Astronomers are now hunting for the remnants of the neutron star collision that gave Earth its precious metals. This is a project being led by physicists at Columbia University. They are assuming a single source for this ‘creative explosion’. It could be that their research will lead them to more than one source although most of the evidence points to an event that took place 100 million years before our solar system formed.
Gaia – Is Seeing Believing

Item selected by the Energy Syndicate
The European Space Agency have reported unusual gravitational lensing from a binary system observed by the Gaia satellite. This was first detected by the Photometric Science Alerts programme maintained by Cambridge University.The initial observation of unusual and sudden brightness coming from a binary star system was investigated further over a period of almost a year. Scientists observed the star getting significantly brighter and then suddenly loosing its intensity over a period of just one day. This type of behaviour is very unusual and did not fit with any record of other observations or other similar types of increase in luminosity such as supernova.
The investigating scientists are assuming that the phenomenon is due to gravitational micro-lensing – an effect that distorts light due to gravitational forces upon spacetime. Over the period of just a few months the effect happened five times.
The Gaia satellite has been responsible for seeing this happen in ‘realtime’. The project scans the whole sky and is likely to see many more events that do not fit current models or understanding. In the future the events it has observed may be the norm to many in the world of science but what would happen if the observation discussed above is a unique moment. Does the work of the scientists make the event a special event or does it trigger an ongoing debate about the cause?

As we look up into the night sky, whether with the naked eye or using equipment, can we be sure that we understand what we are looking at? A bright star in the sky seen by many could be the light of just one star finding its way directly to us but may also be a mix of other light resulting from gravitational lensing or a mirror image that so far has remained unobserved.
For thousands of years our ancestors reported sightings in the sky that modern science has all but bludgeoned the mystery and romance out of. The star of Bethlehem for example: the explanations are plentiful but rarely consider a unique event. Gaia has observed an unusual and possibly unique event – if it had been a record written by someone hundreds of years ago the majority of science would have explained it away in a convincing yet wholly incorrect way.
Is seeing believing?
Earth Made – Mars Made
Item by David - The Energy Syndicate

Missions to Mars are being planned by NASA and ESA. Manned missions are complex. The welfare of the crews is important with a great deal of emphasis being put on psychological support. The crews train in isolated tests in the Antarctic to assess psychological impact.
Life on Earth has grown over millions of years. The psychology of humans is not a condition of an individual but rather a product of the evolution of life. Different people exhibit different traits that fall within certain parameters, all creations of the evolution of life here on Earth are a product of our existence here amidst all aspects of life.
If a human presence was to develop on Mars for example – would the psychological traits of a colony change due to the fact that they are on Mars and no longer cocooned in the embrace of mother Earth i.e. A psychology that is Mars made.
In October (2019), I was in conversation with the Director of the European Space Agencies study on developing techniques for psychological support of crews for exploration missions to Mars. I raised the above question, asking if this potential has been part of their research and testing considerations. Although there was an understanding of the Earth Made – Mars Made aspect, most of the focus of ESA in this area is on maintaining links and connections for crews with Earth. It will require colonising ‘guinea pigs’ in the future to be able to truly quantify the transforming aspects that living on another planet may have upon a group – Man on Mars or Man transforming into Martians?




